Home » Plastic Polymers
What Are Plastic Polymers?
Plastic polymers are a class of materials primarily composed of polymeric compounds, with added plasticizers, stabilizers, lubricants, fillers, and other additives. Under certain temperature and pressure conditions, it can be molded and maintains its shape stably after molding. Chemically, the core of plastic resin is the polymer, a large molecule compound composed of many repeating monomers linked by covalent bonds.
The main components of plastic is plastic polymer. Plastic polymers refer to polymer compound that has not mixed with various additives. The basic properties of plastics are mainly determined by the nature of the resin, additives also play an important role.
Plastic Polymers for Sale in Our Company
| Name | Abbreviation | MF | CAS NO. |
| Polypropylene | PP | (C3H6)n | 9003-07-0 |
| Polyethylene | PE | (C2H4)n | 9002-88-4 |
| High Density Polyethylene | HDPE | (C2H4)n | 9002-88-4 |
| Low Density Polyethylene | LDPE | (C2H4)n | 9002-88-4 |
| Linear Low Density Polyethylene | LLDPE | (C2H4)n | 9002-88-4 |
| Polyvinyl Chloride | PVC | (C2H3CL)n | 9002-86-2 |
| Polyester Resin | PET Resin | H(OCH2CH2OCOC6H4CO)nOCH2CH2OH | 25038-59-9 |
Would like The Quotation?
Leave your demands in detail here(including the model, package, brand, quantity), we will reply you quickly.
Brands We can Supply
Would like The Quotation?
Leave your demands in detail here(including the model, package, brand, quantity), we will reply you quickly.
Classification by Processing Performance: Thermoplastic Resins vs. Thermosetting Resins
What are Thermoplastic Resins?
Thermoplastic resins are plastic resins that soften and melt upon heating, and solidify upon cooling, a process that can be repeated. Their molecular structure is typically linear or branched, with molecular chains linked by van der Waals forces or hydrogen bonds, and no chemical cross-linking bonds. When heated, molecular chain movement intensifies, intermolecular forces weaken, and the material softens and melts. Upon cooling, molecular chain movement slows, intermolecular forces recover, and the material solidifies again.
The core advantages of thermoplastic resins are their recyclability, simple processing, and high production efficiency. They are currently the world’s largest and most widely used category of plastic resins, accounting for over 80% of global plastic resin production.
- Polyethylene PE Polymer
- Polypropylene PP Polymer
- PVC Resin
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Polystyrene PS Polymer
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene ABS
- Polyoxymethylene POM Polymer
- Polycarbonate PC Polymer
The output of polyethylene polymer is the highest in the plastics industry, including low density, high density, and linear density polyethylene. PE polymer is non-toxic, odorless, white or milky white, soft, translucent marble-like granulars. It is a kind of crystalline plastic.
The water absorption of polyethylene plastic polymers is extremely small, and the dielectric properties have nothing to do with temperature and humidity. Therefore, polyethylene polymer is the most ideal high-frequency electrical insulation material, and only polystyrene, polyisobutylene and polytetrafluoroethylene can compare with it in terms of dielectric properties.
HDPE can be used to make plastic pipes, plates, ropes, and low-load parts such as gears and bearing. LDPE is often used to make plastic films, hoses, plastic bottles, insulating parts and cable sheaths in the electrical industry.
Polypropylene polymer is colorless, odorless and non-toxic. It looks like polyethylene, but is more transparent and lighter than polyethylene. It is non-absorbent, has good gloss and is easy to color.
PP polymer has all the excellent properties of PE, such as excellent dielectric properties, water resistance, chemical stability, and is suitable for forming and processing. However, its yield strength, tensile strength, compressive strength and hardness and elasticity are better than polyethylene plastic polymers. In addition, it has good heat resistance and can be sterilized at temperatures above 100℃. PP polymer has good high-frequency insulation performance. It doesn’t absorb water, so its insulation performance isn’t affected by humidity, but it is easy to depolymerize and age under the action of oxygen, heat and light.
Polypropylene polymer can be used for various mechanical parts such as flanges, joints, pump impellers, auto parts and bicycle parts. It can be used as the pipeline for water, steam, various acids and alkalis, the lining and surface coating of chemical containers and other equipment. It can also be used in the pharmaceutical industry.
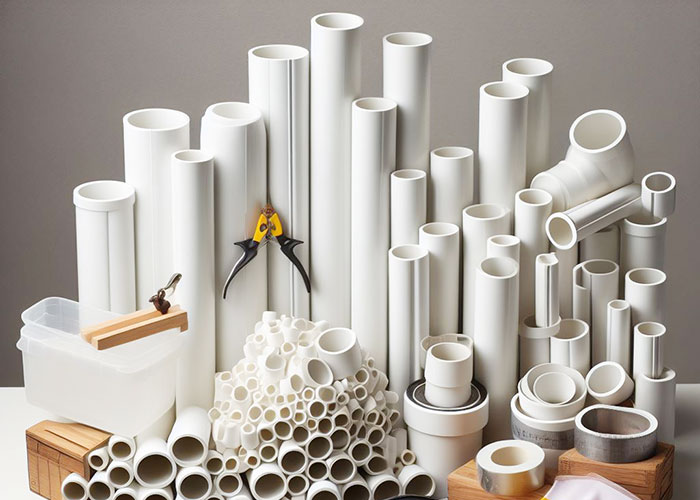
Polyvinyl chloride resin is white or light yellow powder, and becomes transparent block after granulation. By adding different additives according to different uses, PVC plastic polymer parts can exhibit different physical and mechanical properties. Adding an appropriate amount of plasticizer to PVC resin can make a variety of hard and soft products.
Due to the high chemical stability, polyvinyl chloride polymer can be used to make anti-corrosion pipes, pipe fittings, oil pipelines, centrifugal pumps and blowers, etc.
Polyvinyl chloride hard boards are widely used in the production of various storage tank linings, corrugated boards for buildings, door and window structures, wall decorations and other building materials. Due to its good electrical insulation properties, it can be used in the electrical and electronic industries to manufacture sockets, plugs, switches and cables. In daily life, it is used to make sandals, raincoats, toys and artificial leather.
Combining the properties of general-purpose and engineering plastics, it possesses good transparency, mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. It is mainly used for fibers, bottles, food packaging films, and engineering products.
Polystyrene is the third largest plastic species after polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene. PS polymer is colorless, transparent, shiny, non-toxic and tasteless. It is currently the most ideal high-frequency insulating material. Polystyrene has low heat resistance and can only be used at low temperatures. It is hard and brittle, and plastic parts are prone to cracking due to internal stress. Polystyrene has good transparency, high light transmittance, and its optical performance is second only to plexiglass. It has excellent coloring ability and can be dyed into various bright colors.
PS polymer can be used industrially as instrument casings, lampshades, chemical instrument parts, transparent models, etc. It is used as a good insulating material, junction box, battery box in electrical aspects. In daily necessities, it is widely used in packaging materials, various containers, toys, etc.
ABS polymer is a copolymer of three monomers of acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene. Acrylonitrile makes ABS have good surface hardness, heat resistance and chemical corrosion resistance, butadiene makes ABS tough, and styrene makes it have excellent formability and coloring performance.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene polymer is used in the mechanical industry to manufacture gears, pump impellers, bearings, handles, pipes, motor casings, instrument casings, instrument panels, water tank casings, battery tanks, refrigerators and refrigerator linings. In the automobile industry, ABS is used to make car fenders, handrails, hot air conditioning ducts, heaters, etc. ABS sandwich panels can also be used to make car bodies. ABS can also be used to make water meter cases, textile equipment, electrical parts, cultural, educational and sporting goods, toys, electronic organ and cassette player casings, food packaging tableware, pesticide sprayers and furniture.
Polyoxymethylene polymer is a thermoplastic engineering plastic with excellent performance developed after nylon. Polyoxymethylene resin is white powder, after granulation, it becomes light yellow or white, translucent and glossy hard particles. POM has high tensile and compressive properties and outstanding fatigue resistance, and is especially suitable for making wear-resistant transmission parts such as bearings, cams, rollers, rollers, and gears.
POM polymer has stable size, low water absorption, excellent anti-friction, wear-resistant properties, torsion resistance, and outstanding resilience. It can be used to manufacture plastic spring products.
It is generally insoluble in organic solvents at room temperature, resistant to aldehydes, ethers, ethers, hydrocarbons, weak acids, weak bases, gasoline and lubricating oils, but not resistant to strong acids, and has good electrical insulation properties.
It can also be used to manufacture automobile dashboards, carburetors, various instrument shells, covers, boxes, chemical containers, pump impellers, blower blades, switchboards, coil seats, various oil pipelines, etc.
Polycarbonate polymer is a colorless and transparent granular. PC polymer is a thermoplastic engineering plastic with excellent performance. It is tough and rigid, and its impact resistance ranks among the best among thermoplastics. Polycarbonate formed parts can achieve very good dimensional accuracy and maintain their dimensional stability over a wide temperature range. Polycarbonate plastic polymer has a low water absorption rate and can maintain good electrical properties in a wide temperature range.
In machinery, it is mainly used as various gears, worm gears, worms, racks, cams, bearings, various shells, covers, containers, parts of freezing and cooling devices, etc. In terms of electricity, it is used as motor parts, fan parts, dials, instrument cases, terminal blocks, etc. PS plastic polymer can also be used to make optical parts such as lighting lamps, high-temperature lenses, sight mirrors, and protective glass.
What are thermosetting resins?
Thermosetting resins refer to plastic resins that, under heating or the action of a curing agent, undergo a cross-linking reaction of molecular chains to form a three-dimensional network structure. Once cured, they will not soften or melt upon reheating. They will only decompose and break down. Its molecular structure is initially linear or branched. During curing, the molecular chains form a cross-linked network through covalent bonds, giving the material extremely high rigidity, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.
The core advantages of thermosetting resins are excellent heat resistance and rigidity, good dimensional stability after molding, and resistance to deformation. However, their disadvantages include being non-recyclable, having relatively complex processing techniques, long production cycles, and relatively low output. They are mainly used in specialized fields with high performance requirements.
- Epoxy resin (EP)
- Phenolic resin (PF)
- Unsaturated polyester resin (UPR)
- Polyurethane (PU)
One of the most widely used thermosetting resins, possessing excellent adhesion, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation. A wide variety of curing agents are available, allowing for adjustments to curing conditions to meet different needs. It is mainly used in adhesives, coatings, composite materials, and electronic packaging materials.
Possesses excellent heat resistance, flame retardancy, moisture resistance, and electrical insulation. It is mainly divided into phenolic molding compounds, phenolic resin adhesives, and phenolic foams, used in electrical switches, sockets, brake pads, insulation materials, and wood adhesives.
Possesses good molding processability and can be manufactured into various products through hand lay-up, spraying, and molding processes, with relatively low cost. It is mainly used in fiberglass products, artificial marble, coatings, and adhesives.
Depending on the reactants, it can be divided into polyurethane foam, polyurethane elastomers, and polyurethane coatings, possessing some characteristics of both thermoplastic and thermosetting materials.
What are the main applications of plastic resins?
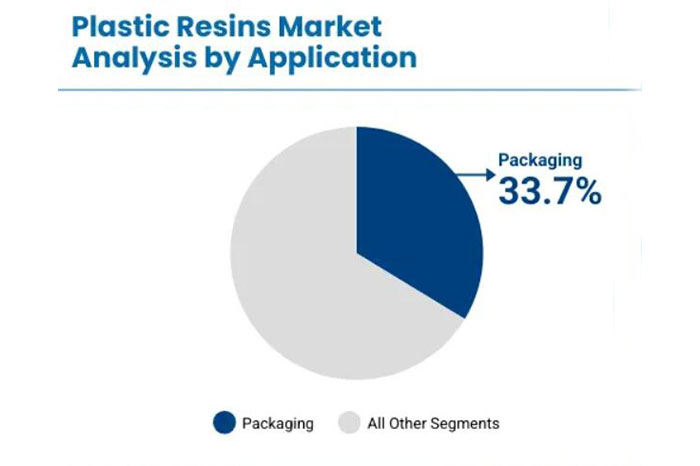
>> Packaging Industry
The packaging industry is the largest application area for plastic resins, accounting for more than 30% of global consumption. It is mainly used for food packaging, pharmaceutical packaging, daily chemical product packaging, and industrial packaging.
Food Packaging: Requires resins with good transparency and barrier properties, meeting food contact material standards. Commonly used resins include PET, PE, PP, PS, and PVC.
Pharmaceutical Packaging: Requires resins with good barrier properties, chemical resistance, and safety. Commonly used resins include PET (pharmaceutical packaging film, capsule shells), PP (pharmaceutical bottles, syringes), PVC (infusion bags, pharmaceutical packaging sheets), and EP (pharmaceutical bottle cap adhesives).
Industrial Packaging: Resins are required to possess good mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and impact resistance to protect industrial products from damage during transportation and storage. Commonly used resins include HDPE (plastic drums, pallets), PP (woven bags, packing straps), PVC (packing sheets), and EPS (cushioning packaging materials).
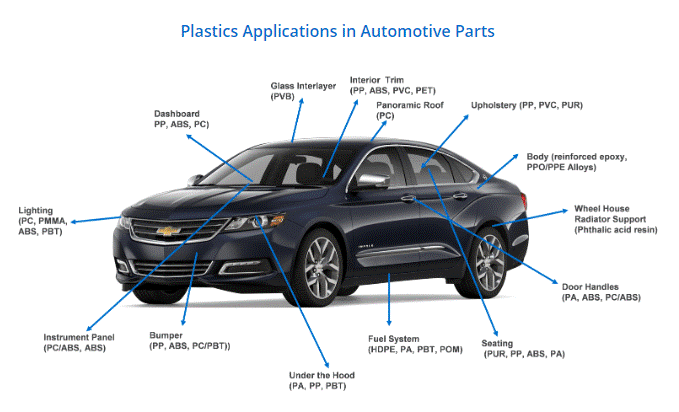
>> Automotive Industry
Automotive plastic resins account for 10%~20% of the weight of automotive parts, mainly used in body structural components, interior parts, exterior parts, and powertrain components.
Body Structural Components: Resins are required to possess high strength, high rigidity, impact resistance, and lightweight properties to reduce body weight and improve fuel economy. Commonly used resins include PP (bumpers, dashboard frames), PA (intake manifolds, gears), PC/ABS alloys (body pillars, door panels), and carbon fiber reinforced composite materials (body frames, chassis components).
Interior Parts: Resins are required to possess good flexibility, wear resistance, environmental friendliness, and aesthetics. Commonly used resins include PP (seat frames, interior trim panels), PVC (car floor mats, door panel coverings), PU (seat foam, steering wheels), and ABS (center console, air vents).
Exterior parts: Resins require good weather resistance, corrosion resistance, scratch resistance, and aesthetics. Commonly used resins include PP (mudguards, wheel arch covers), PC (lamp covers, sunroofs), ABS (rearview mirror housings), and PET (window tinting).
Powertrain components: Resins require good heat resistance, oil resistance, and corrosion resistance. Commonly used resins include PA (oil pipes, seals), PPS (engine cylinder head gaskets, sensor housings), and PEEK (high-temperature bearings, seals).
>> Electronics and electrical appliance industry
The performance requirements for plastic resins in the electronics and electrical appliance industry mainly include insulation, heat resistance, flame retardancy, dimensional stability, and aesthetics. Plastic resins are widely used in the housings, internal structural components, insulating materials, and connectors of electronic devices.
Housings and Structural Components: Resins are required to possess good insulation, heat resistance, flame retardancy, dimensional stability, and aesthetics. Commonly used resins include ABS (computer cases, TV housings), PC (mobile phone housings, monitor housings), PP (appliance bases, housings), and PVC (wire and cable sheaths).
Insulation Materials: Resins are required to possess excellent insulation, heat resistance, and weather resistance. Commonly used resins include EP (circuit boards, insulating varnish), PF (electrical switches, sockets), PVC (wire insulation), and silicone resin (high-temperature insulation materials).
Connectors and Plugs: Resins are required to possess good insulation, mating resistance, and dimensional stability. Commonly used resins include PA (connector housings, terminals), PC (plugs), and PBT (connector frames).

>> Construction Industry
The application of plastic resins in the construction industry is mainly concentrated in building materials, decorative materials, and waterproofing and sealing materials. It has advantages such as being lightweight, durable, easy to apply, and low-cost.
Building Structure and Decoration Materials: Commonly used resins include PVC (door and window profiles, flooring, ceilings), PP (plastic pipes, sheets), PC (polycarbonate sheets, solid polycarbonate sheets), EPS (insulation boards), and PU (rigid foam insulation materials).
Waterproofing and Sealing Materials: Resins are required to have good waterproofing, sealing properties, weather resistance, and corrosion resistance. Commonly used resins include PU (waterproof coatings, sealants), EP (waterproof adhesives), PVC (waterproof membranes), and styrene-butadiene rubber (sealing strips).
Water Supply and Drainage Systems and Piping Systems: Resins are required to have good corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance, low fluid resistance, and long service life. Commonly used resins include UPVC (water supply and drainage pipes, conduit pipes), HDPE (water supply pipes, gas pipes), and PPR (hot and cold water pipes).

>> Textile Industry
Synthetic fibers made from plastic resins are important raw materials for the textile industry, such as PET, PA, and PP.
PET has high strength, good abrasion resistance, and is easy to dye, and is widely used in clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics.
PA has good elasticity and excellent abrasion resistance, and is commonly used in socks, underwear, and sportswear.
PP is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, and is commonly used in non-woven fabrics, carpets, and industrial filter cloths.
>> Medical device industry
It requires resins with good biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and safety (non-toxic and non-allergenic). Commonly used resins include PP (syringes, infusion sets), PVC (infusion bags, urinary catheters), PC (medical device shells, artificial lenses), and PEEK (artificial bones, joints).
>> Agricultural industry
Commonly used resins include PE (agricultural film, irrigation pipes), PP (woven bags, seedling trays), and PVC (agricultural hoses).
PE agricultural film can increase soil temperature, retain moisture, and promote crop growth, making it an important production material in modern agriculture.
PE irrigation pipes have good corrosion resistance and low fluid resistance, enabling water-saving irrigation.
PP woven bags have high strength and good weather resistance, and are commonly used for packaging agricultural materials such as grains and fertilizers.
>> Military and aerospace industries
Resins are required to possess high temperature resistance, radiation resistance, high strength, and lightweight. Commonly used resins include carbon fiber reinforced composites (aircraft fuselages and wings), PEEK (aero-engine components and spacecraft structural parts), PI (high-temperature insulation materials and spacecraft coatings), and EP (missile casings and satellite structural parts).
FAQs about Plastic Polymers
What Are Formation Principle of Plastic Resin
The formation process of plastic resin is essentially a polymerization reaction, where monomer molecules are chemically linked to form polymer chains. Based on different reaction mechanisms, polymerization reactions are mainly divided into two categories.
Addition polymerization. Add monomer molecules to each other to form polymer chains by opening unsaturated bonds such as double and triple bonds. No small molecule byproducts are generated during this reaction. Common resins include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene (PS), all produced through addition polymerization. For example, under the action of a catalyst, the double bonds of ethylene molecules break to form active centers, which then sequentially connect with other ethylene molecules to form a linear polyethylene macromolecule.
Condensation polymerization. It refers to the formation of polymer chains through the condensation reaction between monomer molecules, while simultaneously generating small molecule byproducts such as water, alcohols, and ammonia. This type of reaction typically requires monomer molecules to possess two or more functional groups (such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, and amino groups). Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide (PA, nylon), epoxy resin (EP), and polyurethane (PU) are all produced through condensation polymerization.
What are the excellent properties of plastic resins?
Lightweight and high strength: The density of plastic resins is typically between 0.9 and 2.0 g/cm³, far lower than that of metals and ceramics. However, the specific strength of some high-performance plastics can exceed that of metallic materials, making them suitable for aerospace, automotive lightweighting, and other fields.
Good plasticity and processability: Under certain temperature and pressure conditions, plastic resins can be processed into various shapes through injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, calendering, and other processes. The processing consumes relatively little energy, making it suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Excellent Chemical Stability: Most plastic resins exhibit good corrosion resistance to acids, alkalis, salts, and other chemicals, and are not easily oxidized or decomposed, making them suitable for applications requiring chemical resistance, such as chemical equipment, pipelines, and food packaging.
Good Insulation and Thermal Insulation Properties: Plastic resins are excellent electrical insulators, suitable for insulating shells in electronic appliances, and sheathing for wires and cables. Simultaneously, their low thermal conductivity provides excellent thermal insulation, making them widely used in building insulation materials and appliance insulation layers.
High Cost Control: Most general-purpose plastic resins have widely available raw materials and mature production processes, resulting in relatively low production costs, meeting the needs of large-scale consumer products.
How To Choose The Right Plastic Resin
Selection of resin varieties. The choice of plastic resin should be the one with the performance closest to the purpose of modification, so as to save the amount of additives added.
Selection of resin grades. Different grades of the same plastic resin have great differences in performance, and the grade closest to the purpose of modification should be selected.
Selection of resin fluidity. The viscosity of each plasticized material in the formula should be close to ensure the processing fluidity. For materials with widely different viscosities, a transition material should be added to reduce the viscosity gradient.
Consider the relationship between processing methods and fluidity. Different types of plastic resins have different fluidities. The same kind of plastic polymer also has different fluidity, mainly because of the different distribution of molecular mass and molecular chain. Different processing methods require different fluidity requirements for plastic resins.
What Are Classifications of Plastic Polymers
There are many classification methods of resins. In addition to being divided into natural resins and synthetic resins according to the source of the resins, they can also be classified according to the synthesis reaction and main chain composition.
Classified by plastic polymer synthesis reaction. According to this method, plastic polymers can be divided into addition polymers and condensation polymers. Addition polymer refers to a polymer produced by addition polymerization, and the chemical formula of its chain link structure is the same as that of the monomer. Polycondensate refers to a polymer produced by condensation polymerization, the chemical formula of its structural unit is different from that of the monomer.
Classified according to the main chain composition of plastic resin molecules. According to this method, plastic resins can be divided into carbon chain polymers, hetero chain polymers and elemental organic polymers. Carbon chain polymers refer to polymers in which the main chain is entirely composed of carbon atoms. Heterochain polymers refer to polymers whose main chain is composed of atoms of two or more elements such as carbon and oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Elemental organic polymers mean that the main chain does not necessarily contain carbon atoms, and is mainly composed of atoms of elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminum, titanium, boron, sulfur, and phosphorus.
What are the main raw materials for plastic resins?
① Petroleum-based raw materials: Currently the mainstream source, based on petroleum and natural gas, refined to obtain monomers such as ethylene, propylene, and benzene, which are then used to synthesize most general-purpose plastics such as PE, PP, and PVC.
② Bio-based raw materials: Renewable materials, such as starch, cellulose, vegetable oils, and microbial fermentation products, are used to produce biodegradable plastic resins (such as PLA (polylactic acid) and PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates), representing an important direction for environmentally friendly materials.
What is the significance of the "molecular weight" and "molecular weight distribution" of plastic resins?
Molecular weight is an indicator of the length of polymer chains and directly affects resin properties. Higher molecular weight results in better tensile strength, impact strength, and other mechanical properties, but reduced processing fluidity. Conversely, lower molecular weight results in better fluidity and easier processing, but weaker mechanical properties.
Molecular weight distribution refers to the proportion of molecular chains of different lengths in the resin. Resins with a narrow distribution have more uniform properties and better processing stability. Plastic resins with a wide distribution cater to different processing needs, but their properties fluctuate more.
What is the MFR of plastic polymers?
Melt flow rate (MFR, unit: g/10min) is a core indicator for measuring the processing fluidity of resin. It refers to the mass of resin that passes through a standard capillary tube within 10 minutes under specified temperature and pressure.
A higher MFR indicates better resin fluidity, making it easier to mold through processes such as injection molding and extrusion (suitable for thin-walled, complex products).
A lower MFR indicates poorer fluidity, but the molded product has higher mechanical strength (suitable for thick-walled, load-bearing products).
For example, high MFR LDPE is suitable for making films, while low MFR HDPE is suitable for making plastic container.
What are the key indicators affecting the heat resistance of plastic polymers?
① Melting point (Tm): The temperature at which thermoplastic resins melt.
② Glass transition temperature (Tg): The temperature at which the resin changes from a “glassy” state to a “highly elastic” state.
③ Heat distortion temperature (HDT): The temperature at which the resin undergoes a certain deformation under a specified load, directly reflecting the upper limit of the service temperature.
What is the weather resistance of plastic resins?
Weather resistance refers to the performance stability of resins in natural environments. Resins with poor weather resistance will discolor, become brittle, crack, age, and experience performance degradation after long-term outdoor use. Their weather resistance can be improved by adding additives (UV absorbers, antioxidants, light stabilizers) or by coating and blending modification (such as blending PP with EPDM to improve weather resistance).
What are the requirements for plastic polymers in different processing techniques?
① Injection molding: Requires moderate resin flow and low molding shrinkage (high dimensional accuracy), suitable for complex-shaped products. Commonly used plastic resins include PP, PE, ABS, PC, and PA.
② Extrusion: Requires uniform resin flow and good thermal stability, suitable for producing pipes, sheets, films, and profiles. Commonly used resins include PE, PP, PVC, and PET.
③ Blow molding: Requires high resin melt strength and good toughness, suitable for producing hollow products (plastic bottles and buckets). Commonly used resins include HDPE, LDPE, PET, and PP.
④ Compression molding: Mostly applicable to thermosetting resins (such as EP and PF), requiring controllable resin curing speed and flowability adapted to the mold.
Which resins can be used in food packaging?
Suitable plastic resins for food contact must meet food contact material safety standards (such as China’s GB 4806 series, EU EFSA, and US FDA), have no harmful monomer migration, be odorless, and possess chemical stability.
① Films, cling films: LDPE, PP (high temperature resistant, microwaveable).
② Beverage bottles, oil bottles: PET (transparent, good barrier properties), HDPE (acid and alkali resistant).
③ Tableware or lunch boxes: PP (heat resistant 100-120℃, microwaveable), PS (transparent lunch boxes, not microwaveable).
④ Food containers: PP, HDPE, stainless steel composite PP.
What are the storage requirements for plastic resins?
① Environment: Store in a dry, well-ventilated warehouse, with a temperature controlled between 15-30℃ and relative humidity ≤60%.
② Packaging: Keep the original packaging sealed to prevent moisture absorption.
③ Keep away from heat sources and direct sunlight. Do not store with acids, alkalis, or solvents.
④ Shelf life: General-purpose plastic resins can be stored for 6-12 months in sealed containers. Engineering plastics are recommended to be used within 3-6 months. Performance needs to be retested after the shelf life.
What factors affect the price of plastic resins?
① Upstream raw materials: Fluctuations in oil and natural gas prices directly affect the cost of petroleum-based resins such as PE and PP. Prices of bio-based raw materials affect the prices of PLA and PHA.
② Market supply and demand: Peak downstream demand drives up prices, while overcapacity leads to price declines.
③ Policy factors: Environmental protection production restrictions, import tariffs, and plastic bans, etc.
④ Logistics costs affect the price of imported resins.
- Email: sales@chemategroup.com
- Tel: 0086-371-60921621
- Whatsapp: +86 18624832876
- Wechat: +86 18624832876
- ADD: NO.80 PUHUI ROAD,ZHENGZHOU CITY, HENAN PROVINCE, CHINA




























